Sertraline
The full, clinically endorsed dose recommendation should be obtained from Lareb.
Rationale for drug selection
Sertraline is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) widely used for antenatal depression and anxiety disorders. Because pregnancy alters the activity of drug metabolizing enzymes, dose-adjustments may be necessary to maintain effective concentrations during pregnancy.
Pharmacokinetics of sertraline in pregnancy
Sertraline is mainly metabolized by hepatic enzymes such as CYP2C19, CYP3A4 and CYP2D6. While the activity of CYP2C19 is decreased during pregnancy, the activity of CYP3A4 and CYP2D6 is significantly elevated. The majority of the pharmacokinetic studies show reduced maternal plasma concentrations of sertraline during the second and third trimester. The extent of reduction in maternal plasma concentration varies widely, which is likely explained by genetic variations in hepatic enzyme activity. As a result, some pregnant women may benefit from an increased dosage when a reduced effect of sertraline is observed. Studies show that sertraline crosses the placenta, with foetal concentrations that are approximately 40% of maternal concentrations. Maternal–foetal PBPK models were used to asses gestational changes in the maternal plasma concentration of sertraline and explore dosing scenarios for different genetic variations of hepatic enzyme activity. These models provided useful insights for dosing recommendation and supported decision making.
Benefits and risk with proposed dose adjustments
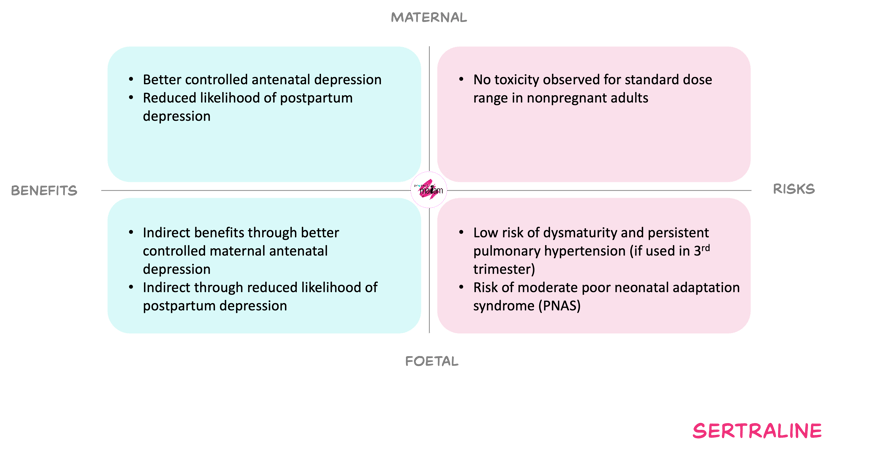
For the mother, cautiously increasing the sertraline dose during pregnancy, if needed, aims to offset pregnancy-related reductions in exposure and thereby sustain control of depression or anxiety. Adequate treatment may reduce risks of relapse, obstetric complications such as prematurity and growth restriction, and subsequent postpartum depression, and may support engagement with care and healthier behaviours. Within the standard adult dose range, serious maternal toxicity is rare, and the “start low, go slow” titration strategy limits the risk of overdosing despite the absence of a clear therapeutic range.
For the foetus, maternal treatment that keeps maternal symptoms controlled may lower the risks associated with untreated maternal depression or anxiety, including adverse perinatal outcomes. However, sertraline crosses the placenta and available data suggest small increases in certain outcomes such as persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn, preterm birth, low birth weight and some cardiac malformations, although absolute risks remain low and findings are not fully consistent. Higher third-trimester doses (> about 100 mg) may be associated with a higher incidence of poor neonatal adaptation syndrome. Long-term neurodevelopmental effects and precise dose–response relationships remain uncertain.
The expected benefits and associated risk of increasing the dose when reduced effect of sertraline is observed during pregnancy.
In short
Sertraline is widely used for depression and anxiety in pregnancy. Pregnancy appears to moderately lower maternal sertraline exposure, especially later in gestation. However, the extension of reduction varies widely across individuals. Based on the weighing of benefits and risks, the working committee derived an appropriate individual dose adjustment. Consult Lareb for the model-informed dosing recommendations.