Nifedipine
The full, clinically endorsed recommendation should be obtained from Lareb.
Rationale for drug selection
Nifedipine is a calcium channel blocker used in pregnancy for hypertension and as a tocolytic. It is known that pregnancy alters pharmacokinetics of drugs. Therefore, dose adjustments might be needed to sustain blood pressure control.
Pharmacokinetics of nifedipine in pregnancy
Nifedipine undergoes hepatic metabolism via CYP3A4. Pregnancy increases CYP3A4 activity and hepatic blood flow, leading to higher clearance. Particularly in the second and third trimester, a decrease of maternal nifedipine concentrations is observed. Peak levels may be 50% lower compared to non‑pregnant individuals. Interindividual variability is large, therefore on an individual basis, it may be considered to increase the dosage of nifedipine. Nifedipine crosses the placenta, exposing the foetus about 78% of the maternal concentration. Several PBPK or semi-mechanistic models have been developed, but due to incomplete pregnancy input data and limited validation they were not used as the primary basis for dosing decisions, therefore clinical PK studies underpinned the conclusions.
Benefits and risk with proposed dose adjustments
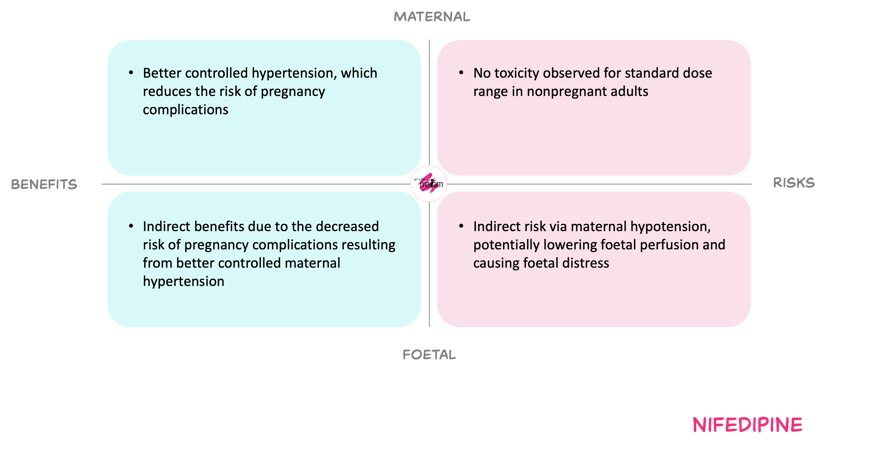
For the mother, the proposed dose adjustments aims to counteract the pregnancy-related increases in clearance and reduced exposure. Increasing the dose may improve blood pressure control and reduce the risk of maternal complications from undertreated hypertension. The main maternal risks are hypotension and vasodilatory adverse effects, particularly at higher doses or with interacting medicines, but these are mitigated by gradual titration according to blood pressure and avoidance of nifedipine as a tocolytic in women who already have hypertension.
For the foetus, improved control of maternal hypertension and effective short-term tocolysis may reduce the risks of placental insufficiency, preterm birth and related neonatal morbidity. Nifedipine crosses the placenta, yet available data do not indicate an increased risk of congenital abnormalities. There is some concern that maternal hypotension could compromise foetal perfusion. The Working Committee balanced the foetal perfusion risk while ensuring effective maternal hypertension treatment.
In short
Pregnancy increases nifedipine clearance and lowers exposure. On an individual basis, it may be considered to increase the dosage of nifedipine to maintain blood pressure control in pregnancy. Based on the weighing of benefits and risks, the working committee derived an appropriate dose adjustment. Consult Lareb for the model-informed dosing recommendations.