Cefuroxime
The full, clinically endorsed dose recommendation should be obtained from Lareb.
Rationale for drug selection
Cefuroxime is a cephalosporin antibiotic used in pregnancy for the treatment of several infections, including pyelonephritis and community-acquired pneumonia. Due to pregnancy-induced changes in the pharmacokinetics of cefuroxime, dose adjustments may be necessary to maintain effective antibiotic concentrations during pregnancy.
Pharmacokinetics of cefuroxime in pregnancy
Cefuroxime is primarily eliminated by the kidneys. Pregnancy increases the glomerular filtration and tubular secretion which lead to an increased renal clearance. Additionally, the extracellular volume expands in pregnancy. Therefore, it is likely that the current clinical doses that are used in pregnancy might fall below the therapeutic range, which may justify an increase in dose, especially during the second and third trimester. Pharmacokinetic studies consistently demonstrate lower maternal plasma levels and shorter half-life compared with non-pregnant women. Maternal PBPK models demonstrate reliable predictions of maternal concentrations in pregnancy, informing alternative dosing strategies, and supporting decision-making. Placental transfer is significant, with cord concentrations around 50–80% of maternal levels.
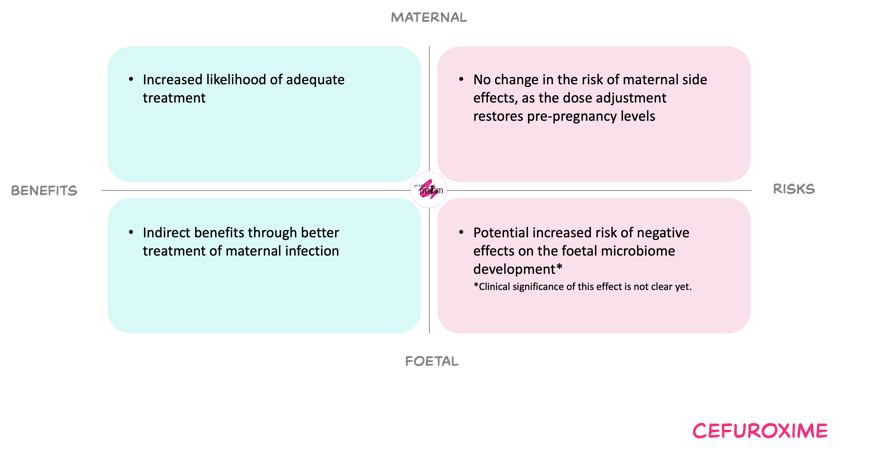
Benefits and risks with the proposed dose adjustments
For the mother, increasing dosing frequency in the second and third trimester aims improve the probability of target attainment and thereby may reduce the risk of persistent infection, sepsis, and infection-related complications such as preterm birth and low birth weight. Reported adverse effects of cefuroxime are usually mild and dose-dependent toxicity appears uncommon at doses within established adult maxima.
For the foetus, undertreated maternal infection is associated with adverse outcomes including preterm birth and low birth weight, so optimising maternal treatment is expected to be beneficial. Cefuroxime does cross the placenta and exposes the foetus, but observational data with cefuroxime and other cephalosporins do not indicate an increased risk of congenital abnormalities. Foetal antibiotic exposure may alter the development of the foetal microbiome, but the clinical impact and any dose–response are unclear. Therefore, the foetal risk from the proposed higher dosing frequency is judged very low.
Overall, the MADAM Working Committee judged that the proposed higher dosing frequency during pregnancy offers a favourable balance of benefits and risks and is acceptable for clinical use.
In short
Cefuroxime is an antibiotic prescribed to treat maternal infections. Pregnancy increases renal clearance and reduces cefuroxime exposure, especially later in gestation. Therefore, increasing the dose during the second and third trimester may improve the likelihood of achieving the therapeutic targets. Based on the weighing of maternal and foetal benefits and risks, a dose increase can be further justified. Consult Lareb for the model-informed dosing recommendations.
