Cefazolin
The full, clinically endorsed recommendation should be obtained from Lareb.
Rationale for drug selection
Cefazolin is widely used for perioperative prophylaxis in pregnancy, including caesarean sections. Due to pregnancy-induced changes in the pharmacokinetics of cefazolin, dose adjustments may be necessary to maintain effective antibiotic concentrations during pregnancy.
Pharmacokinetics of cefazolin in pregnancy
Cefazolin is renally cleared with minimal metabolism in the liver. Pregnancy increases glomerular filtration which can lower drug concentrations in the blood and body tissues. Therefore, the time the drug remains above the minimum level required to effectively treat the infection (MIC), which often originate in the adipose tissue, may be reduced. There were no pharmacokinetic studies comparing cefazolin exposure in pregnant versus non-pregnant women. Population- and maternal physiology-based pharmacokinetic models, indicated that pregnant women weighing over 80kg may need higher doses compared to pregnant women weighing under 80kg, to provide concentrations in adipose tissue above the target MIC. Placental transfer occurs, with foetal levels reaching about 18–45% of the maternal concentration.
Benefits and risks with the proposed drug adjustments
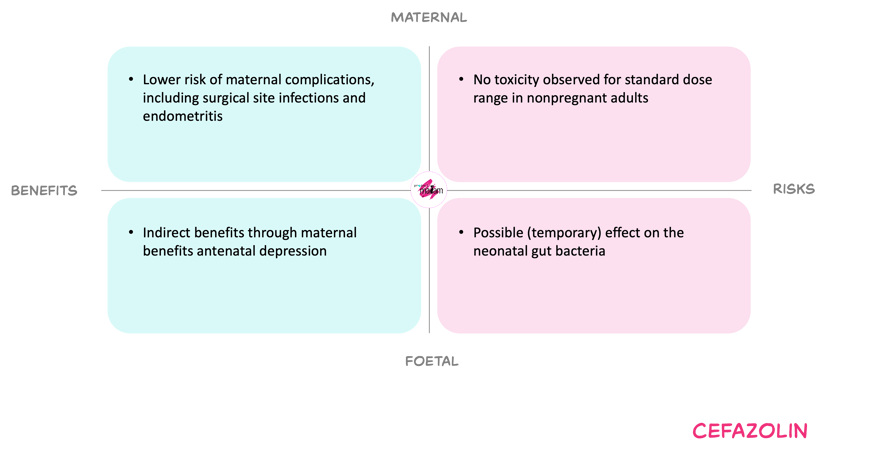
For the mother, increasing the dose in women over 80kg, aims to secure adequate prophylaxis by maintaining effective plasma and adipose tissue concentrations throughout most caesarean and other pregnancy-related surgeries. Underdosing could increase surgical site infections and endometritis. Cefazolin toxicity at these doses is uncommon, and the proposed regimen aligns with doses used safely in non-pregnant surgical patients.
For the foetus, cephalosporins as a group are not associated with an overall increase in congenital anomalies, and cefazolin is considered compatible with pregnancy. Reported concerns about congenital heart defects relate to first-trimester exposure and are not relevant to caesarian prophylaxis. Intrapartum cefazolin use might alter early neonatal gut microbiota composition, but it is unknown if this effect is dose-related, and these changes seem to be transient. Untreated maternal infection carries its own risks for the neonate.
Overall, increasing cefazolin dose in pregnant women weighing over 80 kg, weighing the improved prophylaxis for heavier women against the uncertain, likely small additional microbiome impact, the MADAM Working Committee judged the proposed weight-based regimen and re-dosing strategy to have an acceptable benefit–risk balance for clinical use.
In short
Cefazolin is prescribed as perioperative prophylaxis in pregnancy. Pregnancy increases cefazolin clearance and thereby may reduce adipose tissue exposure. Therefore, dose adjustments may be necessary to maintain effective antibiotic concentrations. Based on the weighing of benefits and risks, the working committee proposed a similar dose in pregnant patients <80 kg than non-pregnant patients, but a higher dose in pregnant women > 80kg. Consult Lareb for the model-informed dosing recommendations.