Amoxicillin
The full, clinically endorsed recommendation should be obtained from Lareb.
Rationale for drug selection
Amoxicillin, alone or with clavulanic acid (ACA), is widely used in pregnancy for the treatment of infections or as antibiotic prophylaxis. Pregnancy-induced changes in amoxicillin pharmacokinetics may necessitate dose adjustments to maintain effective drug concentrations and prevent severe maternal infections that could lead to obstetric and foetal complications.
Pharmacokinetics of amoxicillin in pregnancy
Both renal clearance and the volume of distribution are increased after the first trimester of pregnancy, leading to lower amoxicillin blood levels in pregnant patients compared with non-pregnant adults. Pharmacokinetic (PK) studies, including a physiology-based PK study, show that amoxicillin concentrations are reduced by 15-25% during the second and third trimester. Based on placental-perfusion experiments, the placental transfer of amoxicillin is approximately 30%. During pregnancy, lower amoxicillin doses are often prescribed than in non-pregnant patients. However, as pregnancy reduces amoxicillin exposure, doses similar or even higher than to those used in nonpregnant adults may be more appropriate to avoid concentrations falling below the therapeutic range. Maternal PBPK models provided evidence on the influence of gestational age on the pharmacokinetics changes of amoxicillin in pregnancy and supported decision-making.
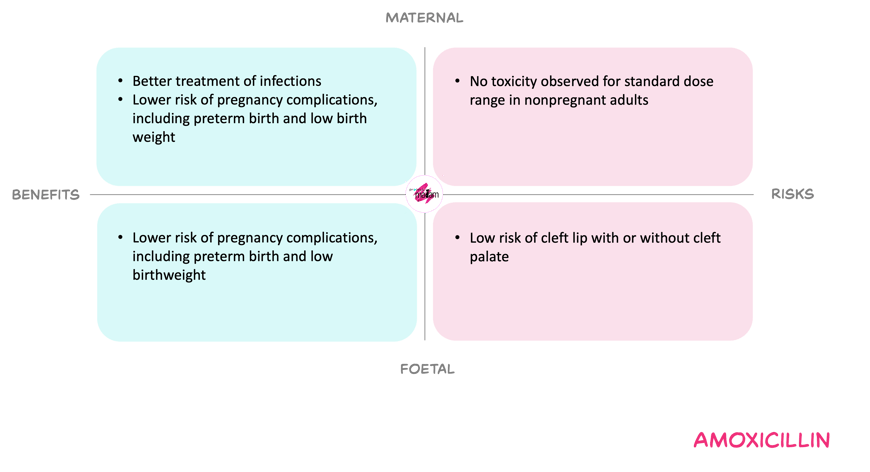
Benefits and risks with the proposed dose adjustments
For the mother, adjusting treatment doses of amoxicillin in pregnancy to match non-pregnant regimens is expected to counteract pregnancy-related reduction of amoxicillin exposure. Thereby reducing the risk of subtherapeutic exposure and treatment failure. At these doses, maternal toxicity appears limited, while untreated or undertreated infection in pregnancy carries substantial complications.
For the foetus, dose adjustments may modestly increase foetal antibiotic exposure. Large datasets on amoxicillin(-clavulanic acid) use in pregnancy do not suggest an increased overall risk of congenital malformations. A small study reported possible link with cleft lip and/or palate after first-trimester amoxicillin, but the results have not been confirmed in larger studies. At the same time, inadequate maternal infection treatment may increase risks of preterm birth, neonatal infection, and cerebral abnormalities.
Overall, the Working Committee considered that the benefit of avoiding underdosing and related complications outweighs the relatively small and manageable risks.
In short
Amoxicillin is given to treat infections during pregnancy. Pregnancy increases clearance and lowers levels in the body. Therefore, it is not justified to prescribe lower doses during pregnancy to nonpregnant individuals. Similar or even higher doses may be needed. Based on the weighing of benefits and risks, such adjustments seem warranted. Consult Lareb for the model-informed dosing recommendations.
